Juanita Fragua
1935-2023
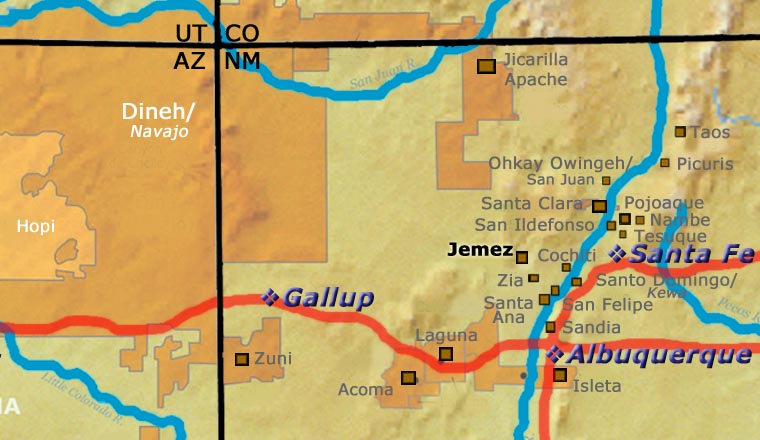
Jemez

"The big ones I push out from inside and groove them on the outside. I have a new one I call the 'oval melon,' grooved only on one side."
Juanita Fragua was born into Jemez Pueblo in March 1935. Her mother was Rita Casiquito Magdalena, a woman from Zia Pueblo. Rita was an experienced Zia potter and, after making adjustments for Jemez clay, taught others at Jemez Pueblo how to make pottery. Later in life Juanita recognized Benina Shije, a sister Corn clan member from Zia, as also being important in the revival of pottery making at Jemez. The pottery tradition at Jemez Pueblo had been virtually extinct for 200 years.
Juanita studied some of the ancient Jemez pottery in the museums of Santa Fe and Albuquerque. She felt their lines were very simple, so she developed more complex designs of her own. She said they were inspired by elements of her Corn clan heritage but she also said, "It's all up here in my head."
Juanita made traditional polished tanware and redware, jars, bowls, cornmeal bowls, vases and wedding vases. Some she decorated with sgraffito work, some she lightly carved, most she painted with traditional designs. Juanita also did embroidery.
Juanita didn't limit herself to traditional Jemez practices either. She studied with Kiowa painter Al Momaday for a while, learning to draw and how to mix paints. Embroiderer Lorencita Bird shared designs and design techniques with her.
Juanita was part of the 1950s wave of pottery revivals passing through the pueblos. She felt free to try everything from sgraffito to carving to micaceous clay. The primary determinant of Jemez style is basically the colors of the base clay, the slips and the paints.
Juanita was a consummate artist and passed her knowledge and perspectives on to her children and many others. Her son, Clifford Fragua, is an internationally known sculptor. Her daughters, Glendora (Daubs) Fragua and Betty Jean Fragua, became award-winning potters.
In 2020, Juanita and Glendora collaborated on a piece they submitted to the Heard Museum Guild Indian Arts Fair & Market in Phoenix. It won the First Place ribbon for Classification II - Pottery, Division E - Any design or form with native materials, kiln-fired pottery. Awarded for the collaborative artwork: "Generations."
Juanita's ribbons date back to the 1980 Santa Fe Indian Market. Sadly, she passed on just before Christmas, 2023.
100 West San Francisco Street, Santa Fe, New Mexico 87501
(505) 986-1234 - www.andreafisherpottery.com - All Rights Reserved

Jemez Pueblo
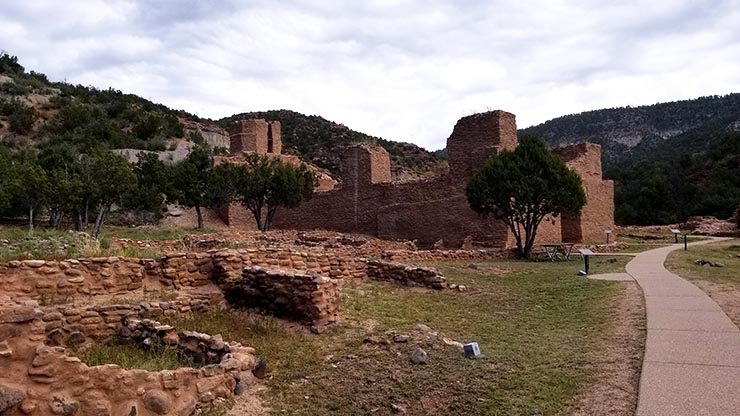

Ruins of San Jose de las Jemez Mission
As the drought in the Four Corners region deepened in the late 1200s, several clans of Towa-speaking people migrated southeastward from the Four Corners area to the Canyon de San Diego area the southern Jemez mountains, in what is now north-central New Mexico. Other clans of Towa-speaking people migrated southwest and settled in the Jeddito Wash area, below Antelope Mesa and southeast of Hopi First Mesa, in what is now northeastern Arizona. The migrations began in earnest in the mid 1200s and were mostly complete by the mid 1300s.
Archaeologist Jesse Walter Fewkes argues that potsherds found in the vicinity of the ruin at Sikyátki (near the foot of Hopi First Mesa) speak to the strong influence of earlier Towa-speaking potters on what became "Sikyátki Polychrome" pottery (Sikyátki was a village at the foot of First Mesa, destroyed before the first Hopi contact with the Spanish in 1540). Fewkes maintained that Sikyátki Polychrome pottery was the finest ceramic ware ever made in prehistoric North America.
Francisco de Coronado and his men arrived in the Jemez Mountains of Nuevo Mexico in 1539. By then the Jemez people had built several large masonry villages among the canyons and on some high ridges in the area. Their population was estimated at about 30,000 and they were among the largest and most powerful tribes in northern New Mexico. Some of their pueblos reached five stories high and contained as many as 3,000 rooms.
Because of the nature of the landscape they inhabited, growing food was very hard. So the Jemez became traders, too, and their people traded goods all over the Southwest and northern Mexico.
The arrival of the Spanish was disastrous for the Jemez and they resisted the Spanish with all their might. That led to many atrocities against the tribe until they rose up in the Pueblo Revolt of 1680 and evicted the Spanish from northern New Mexico. With the Spanish gone, the Jemez destroyed much of what they had built on Jemez land. Then they concentrated on preparing themselves for the eventual return of the hated priests and the Spanish military.
The Spanish returned in 1692 and their efforts to retake northern New Mexico bogged down as the Jemez fought them doggedly for four years. In 1696 many Jemez came together, killed a Franciscan missionary and then fled to join their distant relatives in the Jeddito Wash area. They remained at Jeddito Wash for several years before returning to the Jemez Mountains. As a result of that long ago contact, there are still strong ties between the Jemez and their cousins on Navajo territory at Jeddito. On their return to the Jemez Mountains, the people built the pueblo they now live in (Walatowa: The Place) and made peace with the Spanish authorities.
Some of the Jemez people had been making a type of plainware pottery (simple, undecorated, utilitarian) when they were still in the Four Corners area, while others had developed a distinctive type of black-on-white pottery. In moving to the Jemez Mountains, they brought their knowledge and techniques with them but had to adapt to the different materials available to work with. Over time, the Jemez got better in their agricultural practices and began trading agricultural goods to the people of Zia Pueblo in return for pottery. By the mid-1700s, the Jemez people were producing almost no pottery.
East of what is now Santa Fe is where the ruins of Cicuyé (Pecos) Pueblo are found. Cicuyé was a large pueblo housing up to 2,000 people at its height. The people of Cicuyé, and some in the northern Galisteo Basin, were the only other speakers of the Towa language in New Mexico. When that area fell on increasingly hard times (Apache and Comanche raids, European diseases, drought), Cicuyé was finally abandoned in 1838 when the last 17 residents moved to Jemez. The Governor of Jemez welcomed them and allowed them to retain many of their Cicuyé tribal offices (governorship and all). Descendants of former Cicuyé families still return to the site of their ancestral home every year to perform religious ceremonies in honor of their ancestors.
When general American interest in Puebloan pottery started to take off in the 1960s, the people of Jemez sought to recover that lost heritage. Today, the practice of traditional pottery-making is very much alive and well among the Jemez.
The focus of Jemez pottery today has mostly turned to the making of storytellers, nativities and other figures. Figures are an art form that now accounts for more than three-quarters of their pottery production.
Storytellers are usually grandparent figures with the figures of children attached to their bodies. The grandparents are pictured singing tribal songs and oral histories to their descendants. While this visual representation was first created at Cochiti Pueblo (a site in close geographical proximity to Jemez Pueblo) in the early 1960s by Helen Cordero, it speaks to the relationship between grandparents and grandchildren of every culture. Nativities, corn maidens, singing angels and many different animal forms are also popular among the potters of Jemez.
The pottery vessels made at Jemez Pueblo today are generally not black-on-white. Instead, the potters have adopted many colors, styles and techniques from other pueblos to the point where Jemez potters no longer have one distinct style of their own beyond that which stems naturally from the materials they themselves acquire from their surroundings: it doesn't matter what the shape or design is, the clay itself says uniquely "Jemez."
100 West San Francisco Street, Santa Fe, New Mexico 87501
(505) 986-1234 - www.andreafisherpottery.com - All Rights Reserved

Rita Casiquito Family Tree
Disclaimer: This "family tree" is a best effort on our part to determine who the potters are in this family and arrange them in a generational order. The general information available is questionable so we have tried to show each of these diagrams to living members of each family to get their input and approval, too. This diagram is subject to change should we get better info.
- Rita Casiquito Magdalena
- Juanita Fragua (1935-2023) and Manuel Fragua
- Betty Jean Fragua (1962-2022)
- Clifford Fragua
- Glendora Fragua Daubs (1958- )
- Geronima Shendo and Frank Shendo
- Roberta Shendo (1959- ) and Juan Chavez
- Helen Shendo (1955- )
Some of the above info is drawn from Southern Pueblo Pottery, 2000 Artist Biographies, by Gregory Schaaf, © 2002, Center for Indigenous Arts & Studies
Other info is derived from personal contacts with family members and through interminable searches of the Internet and cross-examination of the data found.
(505) 986-1234 - www.andreafisherpottery.com - All Rights Reserved