
Click or tap to see a larger version
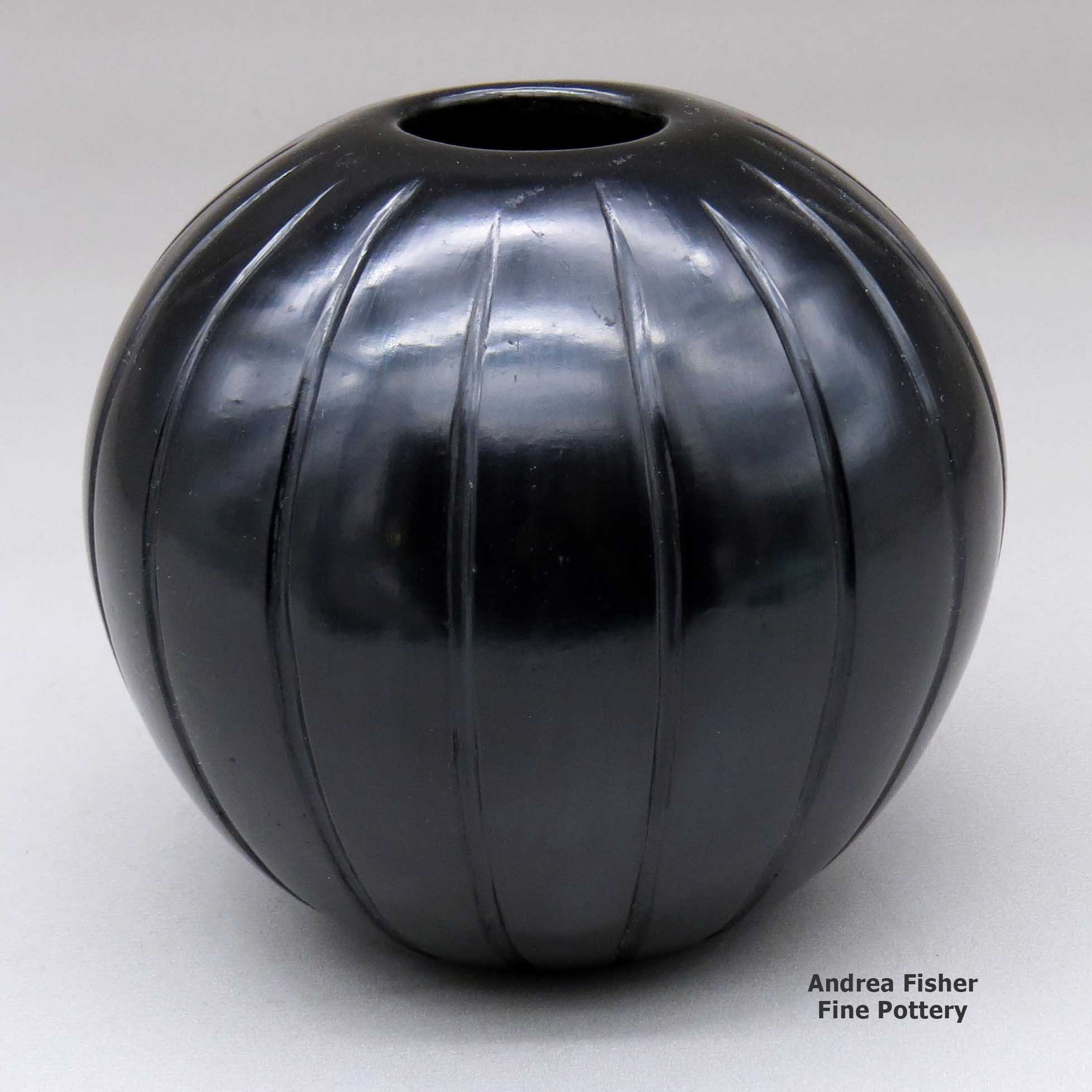
Joy Cain, Santa Clara, A black melon jar lightly carved with 17 ribs
Santa Clara
$ 275
shsc4f531
A black melon jar lightly carved with 17 ribs
4.75 in L by 4.75 in W by 4.5 in H
Condition: Very Good
Signature: Joy Cain Santa Clara Pueblo
Tell me more! Buy this piece!
(505) 986-1234 - www.andreafisherpottery.com - All Rights Reserved
Joy Cain
Santa Clara

Joy Cain was born into Santa Clara Pueblo in 1947. She is the daughter of Willie and Mary Cain, granddaughter of Christina Naranjo. Joy learned how to make pottery through watching and working with her mother and grandmother as she was growing up. Among her siblings are Margie Tanin, Douglas Cain, Billy Cain, Tina Diaz, Warren Cain and Linda Cain.
Joy liked to make redware and blackware wedding vases, jars and bowls. Her favorite design to carve was the avanyu. She was a participant in the Santa Fe Indian Market from about 1985 to about 1998.
As of early 2024, Joy seems to still be living but no longer producing pottery.
Santa Clara Pueblo

Ruins at Puye Cliffs, Santa Clara Pueblo
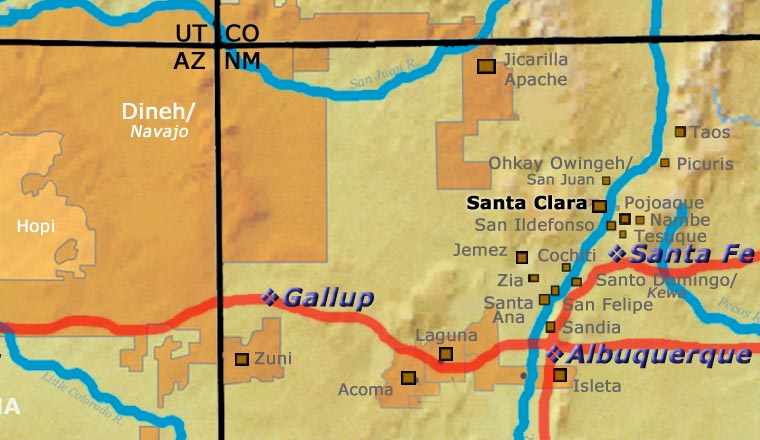
Santa Clara Pueblo straddles the Rio Grande about 25 miles north of Santa Fe. Of all the pueblos, Santa Clara has the largest number of potters.
The ancestral roots of the Santa Clara people have been traced to ancient pueblos in the Mesa Verde region in southwestern Colorado. When that area began to get dry between about 1100 and 1300 CE, some of the people migrated eastward, then south into the Chama River Valley where they constructed several pueblos over the years. One was Poshuouinge, built about 3 miles south of what is now Abiquiu on the edge of the Jemez foothills above the Chama River. Eventually reaching two and three stories high, and with up to 700 rooms on the ground floor, Poshuouinge was occupied from about 1375 CE to about 1475. Drought then again forced the people to move, some of them going to the area of Puye (on the eastern slopes of the Pajarito Plateau of the Jemez Mountains) and others downstream to Ohkay Owingeh (San Juan Pueblo, along the Rio Grande). Beginning around 1580 CE, drought forced the residents of the Puye area to relocate closer to the Rio Grande and they founded what we now know as Santa Clara Pueblo on the west bank of the river, with San Juan Pueblo to the north and San Ildefonso Pueblo to the south.
In 1598 the seat of Spanish government was established at Yunque, near San Juan Pueblo. The Spanish proceeded to antagonize the Puebloans so badly that that government was moved to Santa Fe in 1610, for their own safety.
Spanish colonists brought the first missionaries to Santa Clara in 1598. Among the many things they forced on the people, those missionaries forced the construction of the first mission church around 1622. However, like the other pueblos, the Santa Clarans chafed under the weight of Spanish rule. As a result, they were in the forefront of the Pueblo Revolt of 1680. One Santa Clara resident, a mixed black and Tewa man named Domingo Naranjo, was one of the rebellion's ringleaders. However, the pueblo unity that allowed them to chase the Spanish out fell apart shortly after their success, especially after Popé died.
When Don Diego de Vargas came back to the area in 1694, he found most of the Santa Clarans on top of nearby Black Mesa (with the people of San Ildefonso). A six-month siege didn't subdue them so finally, the two sides negotiated a treaty and the people returned to their pueblos. However, successive invasions and occupations by northern Europeans took their toll on all the tribes over the next 250 years. Then the swine flu pandemic in 1918 almost wiped them out.
Today, Santa Clara Pueblo is home to as many as 2,600 people and they comprise probably the largest per capita number of artists of any North American tribe (estimates of the number of potters run as high as 1-in-4 residents).
Today's pottery from Santa Clara is typically either black or red. It is usually highly polished and designs might be deeply carved or etched ("sgraffito") into the pot's surface. The water serpent, (avanyu), is a very common traditional design motif on Santa Clara pottery. Another motif comes from the legend that a bear helped the people find water during a drought. The bear paw has appeared on much of their pottery ever since.
Santa Clara has received a lot of distinction because of the evolving artistry the potters have brought to their craft. Not only did this pueblo produce excellent black and redware, several notable innovations helped move pottery from the realm of utilitarian vessels into the domain of art. Different styles of polychrome redware emerged in the 1920s-1930s. In the early 1960s experiments with stone inlay, incising and double firing began. Modern potters have also extended the tradition with unusual shapes, slips and designs, illustrating what one Santa Clara potter said: "At Santa Clara, being non-traditional is the tradition." (This refers strictly to artistic expression; the method of creating pottery remains traditional).
Santa Clara Pueblo is home to a number of famous pottery families: Tafoya, Baca, Gutierrez, Naranjo, Suazo, Chavarria, Garcia, Vigil, and Tapia - to name a few.


Santa Clara Pueblo at Wikipedia
Pueblos of the Rio Grande, Daniel Gibson, ISBN-13:978-1-887896-26-9, Rio Nuevo Publishers, 2001
Upper photo courtesy of Einar Kvaran, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License
Christina Naranjo Family Tree
Disclaimer: This "family tree" is a best effort on our part to determine who the potters are in this family and arrange them in a generational order. The general information available is questionable so we have tried to show each of these diagrams to living members of each family to get their input and approval, too. This diagram is subject to change should we get better info.
- Christina Naranjo (1891-1980) & Jose Victor Naranjo (1895-1942)
- Mary Cain (1916-2010) & Willie Cain
- Billy Cain (1950-2005)
- Joy Cain (1947-)
- Linda Cain (1949-)
- Autumn Borts (1967-)
- Tammy Garcia (1969-)
- Tina Diaz (1946-)
- Warren Cain (1951-)
- Douglas Tafoya
- Marjorie Tafoya Tanin
- Mary Louise Eckleberry (1921-2003)
- Darlene Eckleberry
- Victor (1958-) & Naomi Eckleberry
- Teresita Naranjo (1919-1999)
- Mildred Moore (Naranjo, 1941-) & Victor Naranjo
- Eldon Moore
- Ernie Moore
- Kelli Moore
- Rick Moore
- Stella Chavarria (1939-)
- Denise Chavarria (1959-)
- Joey Chavarria (1964-1987)
- Sunday Chavarria (1963-)
- Mildred Moore (Naranjo, 1941-) & Victor Naranjo
- Cecilia Naranjo & James Lee McLean
- Sharon Naranjo Garcia (1951-) & Lawrence Atencio (San Juan)
- Ira Atencio (1975-)
- Lawrence Thunder Atencio
- Judy (1962-) & Lincoln Tafoya (1954-)
- Cecilia Fawn Tafoya (1986-)
- Chelsea Tafoya
- Eli Tafoya (1991-)
- Josetta Tafoya (1993-)
- Lincoln A. Tafoya (1989-)
- Linette Tafoya (1989-)
- Sarah Ayla Tafoya (1987-)
- Sharon Naranjo Garcia (1951-) & Lawrence Atencio (San Juan)
- Mida Tafoya (1931-2024)
- Ethel Vigil (1950-)
- Kimberly Garcia (1978-)
- Mike Tafoya (1956-)
- Phyllis Tafoya (1955-) & Matthew Tafoya (1953-)
- Sherry Tafoya (1956-)
- Phyllis & Marlin Hemlock (Seneca)
- Lincoln Tafoya (1954-)
- Ethel Vigil (1950-)
- Edward Mickey Naranjo and Gracie Naranjo (Navajo)
- Edward Mickey Naranjo Jr.
- Teresa Naranjo
- Tracy Naranjo
Some of the above info is drawn from Pueblo Indian Pottery, 750 Artist Biographies, by Gregory Schaaf, © 2000, Center for Indigenous Arts & Studies. Other info is derived from personal contacts with family members and through interminable searches of the Internet.
Copyright © 1998-2025 by



